Carotid Artery Disease
Basic Facts
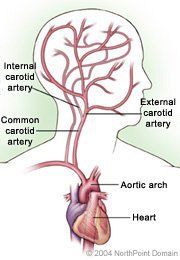
- Carotid artery disease is a form of peripheral arterial disease, or PAD, a disease of the arteries that carry blood away from the heart to the head, torso, arms, and legs.
- Carotid artery disease can prevent blood from reaching parts of the head and brain. This lack of blood can cause shortages of oxygen that can result in transient ischemic attacks or stroke.
- About one-third of the more than 600,000 strokes in the United States every year are the result of blockages originating in the carotid arteries.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Many people with carotid artery disease have no symptoms. Symptoms typically occur once a carotid artery has narrowed by 50 percent, and include:
- Loss or impairment of vision in one eye;
- Weakness, tingling, numbness, or paralysis in the face, arms or legs, usually on one side of the body;
- Sudden loss of coordination; and
- Difficulty swallowing or a sudden inability to speak.
People may experience these symptoms for up to 30 minutes during a TIA.
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
Carotid artery disease is caused by atherosclerosis. The conditions that may predispose a person to carotid atherosclerosis can be inherited. However, other factors that affect the process of carotid atherosclerosis and include:
- Smoking;
- Abnormal levels of blood cholesterol;
- Hypertension (high blood pressure);
- Diabetes mellitus; and
- Being overweight.
- Alcohol abuse.
DIAGNOSIS
Physicians can sometimes diagnose carotid artery disease through taking a patient's medical history and physical examination, which includes listening for a whooshing sound of the turbulent flow of blood as it flows through the carotid artery, called a bruit.
The physician can also diagnose carotid artery disease through tests, including:
- Carotid ultrasound, or echocardiography;
- Magnetic resonance angiography; and
- Angiography.
TREATMENT APPROACH
Lifestyle changes can help people minimize their risk of developing or worsening carotid artery disease that can lead to a stroke. They include:
- Quitting smoking;
- Lowering high blood pressure;
- Reducing high cholesterol;
- Maintaining a healthy weight; and
- Being physically active each day.
- Anticoagulants;
- Antiplatelets;
- Statins; and
- Lipid-lowering agents.
- Angioplasty and stenting; and
- Carotid endarterectomy.
Copyright © 2017 NorthPoint Domain, Inc. All rights reserved.
This material cannot be reproduced in digital or printed form without the express consent of NorthPoint Domain, Inc. Unauthorized copying or distribution of NorthPoint Domain's Content is an infringement of the copyright holder's rights.
